QR code phishing
Are you prepared learning about it?

Quishing, a form of QR-code phishing, deceives individuals into scanning malicious code that steals login credentials or deploys malware. By 2025, it will constitute 1 in 8 credential-harvesting campaigns.
This guide shows you what quishing is, how QR phishing works, and how to stop it: Defining quishing helps us recognize the dangers of QR code phishing. Quishing, a combination of “QR code” and “phishing,” is a deceptive cyberattack tactic where malicious actors exploit QR codes to redirect users to fraudulent websites, steal sensitive data, or install malware.
Unlike traditional phishing tactics that rely on suspicious links or attachments in emails—which can be detected and blocked by email filters - quishing uses QR codes embedded within seemingly harmless images or PDF attachments. Email filters typically scan for known malicious URLs or executable files, but they cannot analyze the content behind a QR code image, making it easier for these threats to bypass detection.
Quishing differs from normal phishing tactics, which usually involve fake emails or text messages. Instead, quishing uses QR codes that appear safe but are actually dangerous. These generated QR codes are often found on restaurant menus, advertisements, or payment screens.
What are Quishing Attacks?
In quishing attacks, a cybercriminal creates a fake QR code that looks safe. When someone scans it using their phone’s camera app, it takes them to a dangerous website. This website might ask them to log in, download something, or give away personal information—like passwords or bank details.
Related articles
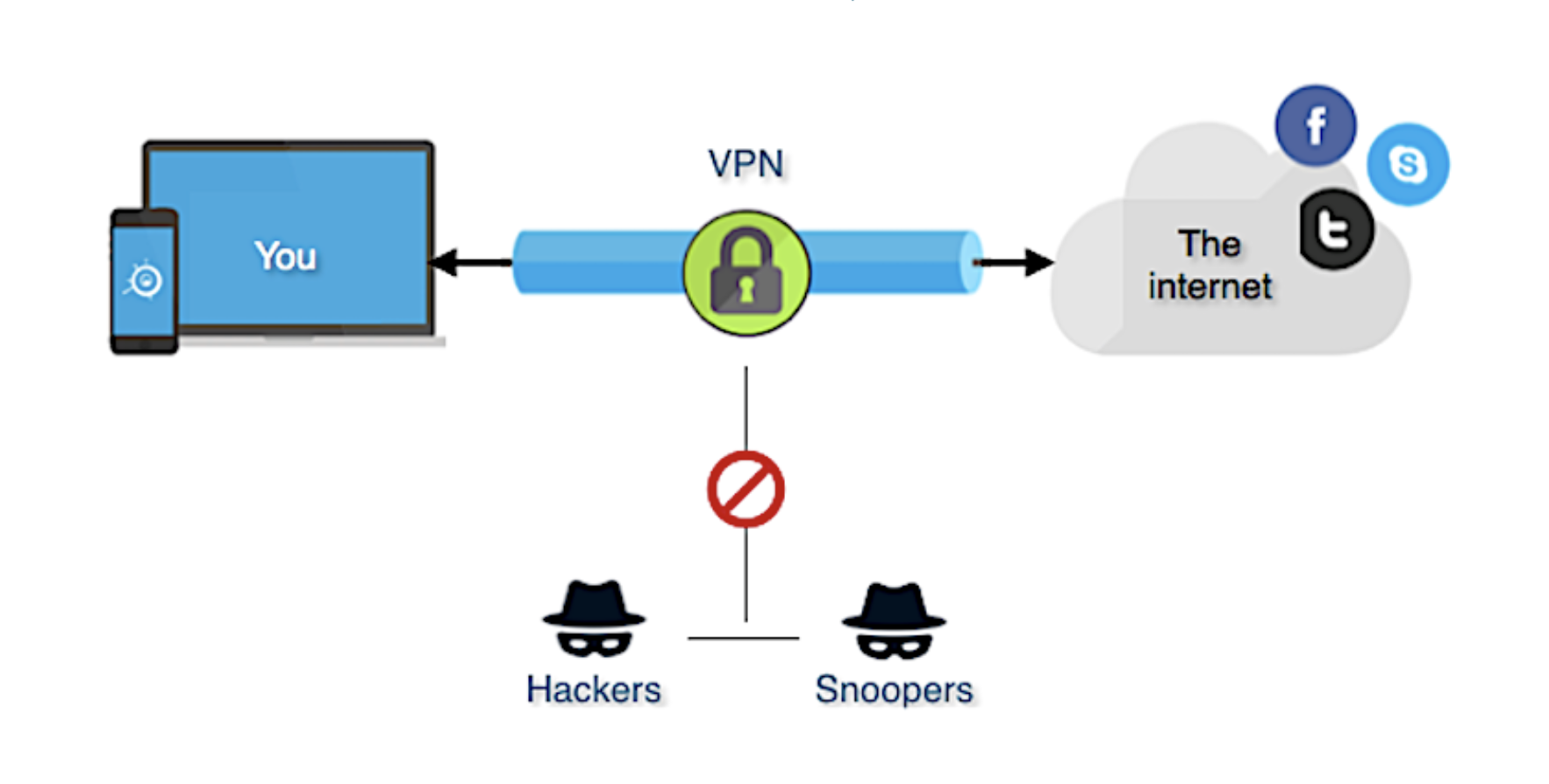
How a VPN works?
Why you should care?
Ataques usando ChatGPT para atingir usuários de MacOS
Desconfie sempre
Avoid SQL Injection in Stored Procedures
In practice using SQL

 Equipe ECODE10.COM
Equipe ECODE10.COM